This project funded by the Long Island Sound Partnership.
Changing Landscape is a project of UConn CLEAR that utilizes land cover maps derived from satellite images to map and quantify land cover change over time. The work presented here uses the National Land Cover Database (NLCD) land cover as input to the analyses and maps that are shared.
About the National Land Cover Database (NLCD)
The U.S. Geological Survey’s (USGS) Land Cover program has leveraged methodologies from legacy land cover projects together with modern innovations in geospatial methods to create the next generation of land cover and land change information. The result is Annual NLCD from 1985 to present.
The Annual NLCD land cover provides a categorical sixteen-class land cover classification system. The land cover product represents the predominant surface state within the mapping year with respect to broad categories of artificial or natural surface
cover.
Map Viewer and Data Dashboards
U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), 2024, Annual NLCD Collection 1 Science Products: U.S. Geological Survey data release, https://doi.org/10.5066/P94UXNTS
Why use NLCD?
Understanding changes in land cover is essential to understanding environmental impacts due to land conversion, natural resource conservation and management, land use planning, and much more. In order to see and analyze land cover and land cover change in Connecticut and the lower Long Island Sound Watershed, UConn CLEAR started the Changing Landscape study. It grew over time and ended with 30 years of land cover (7 dates between 1985 and 2015). The land cover dates were created so that they could be compared for changed. The data and analyses have been invaluable to many users and disciplines.
Due to changes in personnel and technology, UConn CLEAR stopped creating its Changing Landscape land cover with the 2015 dataset. As time passed, the gap grew along with the need for updated land cover with the ability to assess change.
Although the National Land Cover Database (NLCD) has been around for decades, they recently released the Annual NLCD Land Cover which contains annual land cover datasets that can be compared over time. That means Land Cover Change! Game changer! Additionally, the NLCD Land Cover is updated on a predictable schedule by the United State Geologic Survey (USGS). UConn CLEAR has transitioned to using Annual NLCD Land Cover for Changing Landscape Studies. It is called Changing Landscape with NLCD.
National Land Cover Database (NLCD) Classes
Land Cover Classes
Land Cover Classes used in the Map Viewer and Data Dashboard
Aggregated Class |
NLCD Class(es) |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Open Water | Water | |
| Developed | High Intensity Developed, Medium Intensity Developed, Low Intensity Developed | Developed areas with high amounts of impervious surface or impervious surface mixed with other land cover types. Typically found in cities and residential areas. Note that the Developed Class is not the same as the Impervious layer. See FAQs for more information. | |
| Developed Open Space | Developed Open Space | Areas with a mixture of some constructed materials, but mostly vegetation in the form of lawn grasses. These areas most commonly include large-lot single-family housing units, parks, golf courses, and vegetation planted in developed settings for recreation, erosion control, or aesthetic purposes. | |
| Forest | Deciduous Forest, Evergreen Forest, Mixed Forest, Shrub/Scrub, Woody Wetlands | Areas dominated by trees. This class includes shrub/scrub which are shorter trees or shrubs. | |
| Agriculture | Pasture/Hay, Cultivated Crops | Fields of grass or other plants for livestock grazing or production of crops. | |
| Barren | Barren (Rock/Sand/Clay) | Areas of bedrock, desert pavement, scarps, talus, slides, volcanic material, glacial debris, sand dunes, strip mines, gravel pits and other accumulations of earthen material. Generally, vegetation accounts for less than 15% of total cover. | |
| Wetland | Emergent Herbaceous Wetlands | Vegetated areas where the soil or substrate is periodically saturated with or covered with water. | |
| Grass | Grassland/Herbaceous | Areas dominated by grasses and similar low vegetation and not subject to agricultural activities. |
Full NLCD Class Descriptions
| Class Number |
Class |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | Open Water | areas of open water, generally with less than 25% cover of vegetation or soil. | |
| 24 | Developed, High Intensity | highly developed areas where people reside or work in high numbers. Examples include apartment complexes, row houses and commercial/industrial. Impervious surfaces account for 80% to 100% of the total cover. | |
| 23 | Developed, Medium Intensity | areas with a mixture of constructed materials and vegetation. Impervious surfaces account for 50% to 79% of the total cover. These areas most commonly include single-family housing units. | |
| 22 | Developed, Low Intensity | areas with a mixture of constructed materials and vegetation. Impervious surfaces account for 20% to 49% percent of total cover. These areas most commonly include single family housing units. | |
| 21 | Developed, Open Space | areas with a mixture of some constructed materials, but mostly vegetation in the form of lawn grasses. Impervious surfaces account for less than 20% of total cover. These areas most commonly include large-lot single-family housing units, parks, golf courses, and vegetation planted in developed settings for recreation, erosion control, or aesthetic purposes. | |
| 41 | Deciduous Forest | areas dominated by trees generally greater than 5 meters tall, and greater than 20% of total vegetation cover. More than 75% of the tree species shed foliage simultaneously in response to seasonal change. | |
| 42 | Evergreen Forest | areas dominated by trees generally greater than 5 meters tall, and greater than 20% of total vegetation cover. More than 75% of the tree species maintain their leaves all year. Canopy is never without green foliage. | |
| 43 | Mixed Forest | areas dominated by trees generally greater than 5 meters tall, and greater than 20% of total vegetation cover. Neither deciduous nor evergreen species are greater than 75% of total tree cover. | |
| 52 | Shrub/Scrub | areas dominated by shrubs; less than 5 meters tall with shrub canopy typically greater than 20% of total vegetation. This class includes true shrubs, young trees in an early successional stage or trees stunted from environmental conditions. | |
| 71 | Grassland/Herbaceous | areas dominated by graminoid or herbaceous vegetation, generally greater than 80% of total vegetation. These areas are not subject to intensive management such as tilling but can be utilized for grazing. | |
| 81 | Pasture/Hay | areas of grasses, legumes, or grass-legume mixtures planted for livestock grazing or the production of seed or hay crops, typically on a perennial cycle. Pasture/hay vegetation accounts for greater than 20% of total vegetation. | |
| 82 | Cultivated Crops | areas used to produce annual crops, such as corn, soybeans, vegetables, tobacco, and cotton, and perennial woody crops such as orchards and vineyards. Crop vegetation accounts for greater than 20% of total vegetation. This class also includes all land being actively tilled. | |
| 90 | Woody Wetlands | areas where forest or shrubland vegetation accounts for greater than 20% of vegetative cover and the soil or substrate is periodically saturated with or covered with water. | |
| 95 | Emergent Herbaceous Wetlands | areas where perennial herbaceous vegetation accounts for greater than 80% of vegetative cover and the soil or substrate is periodically saturated with or covered with water. | |
| 31 | Barren (Rock/Sand/Clay) | areas of bedrock, desert pavement, scarps, talus, slides, volcanic material, glacial debris, sand dunes, strip mines, gravel pits and other accumulations of earthen material. Generally, vegetation accounts for less than 15% of total cover. |
Full descriptions on the MRLC (Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics Consortium) National Land Cover Database Class Legend and Description page. Note that some class colors have been modified and that some NLCD classes do not occur in the study area including Perennial Ice/Snow, Dwarf Scrub, Lichens, and Moss.
Change To Classes
Change To Classes
| Developed before 1985 | |
| Developed Open Space before 1985 | |
| Water | |
| Undeveloped | |
| Change to Developed between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Change to Developed Open Space between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Other |
Developed is a combination of the NLCD classes of low, medium, and high density developed.
See Land Cover Classes tab for full class descriptions.
Change From Classes
Change From Classes
| Developed before 1985 | |
| Developed Open Space before 1985 | |
| Water | |
| Undeveloped | |
| Agriculture to Developed between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Agriculture to Developed Open Space between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Forest to Developed* between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Forest to Developed Open Space between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Other Classes to Developed between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Other Classes to Developed Open Space between 1985 and 2023 | |
| Other |
Developed is a combination of the NLCD classes of low, medium, and high density developed.
Agriculture is a combination of the Crop and Hay/Pasture classes
Forest is a combination of Deciduous Forest, Coniferous Forest, Mixed Forest, Shrub, and Forested Wetland.
See Land Cover Classes tab for full class descriptions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Original Changing Landscape Land Cover was created and published by UConn CLEAR. The Turf & Grass one is important for Connecticut and is defined below.
| Turf & Grass | A compound category of undifferentiated maintained grasses associated mostly with developed areas. This class contains cultivated lawns typical of residential neighborhoods, parks, cemeteries, golf courses, turf farms, and other maintained grassy areas. Also includes some agricultural fields due to similar spectral reflectance properties. |
The class is yellow on the Changing Landscape Land Cover and did an excellent job of identifying laws, parks, golf courses, and the like.
The National Land Cover Database (NLCD) is the base Land Cover in the new Changing Landscape with NLCD project. The NLCD land cover does not have a turf & grass class. It does have a class called "Developed Open Space" which is one of four classes in the "Developed" family - High Intensity Developed, Medium Intensity Developed, Low Intensity Developed, and Developed Open Space. The Developed Open Space class is defined below.
| Developed Open Space | Areas with a mixture of some constructed materials, but mostly vegetation in the form of lawn grasses. These areas most commonly include large-lot single-family housing units, parks, golf courses, and vegetation planted in developed settings for recreation, erosion control, or aesthetic purposes. |
Although from the definition it sounds like the Developed Open Space class is similar to the Turf & Grass class, they were more different than we hoped. The biggest difference is that rural roads, which are very common in Connecticut, are classified differently. In the original land cover, roads were classified as developed (red) with vegetation along the road. In the NLCD land cover, they are classified as Developed Open Space (light pink).
Visit the Viewer to compare layers and explore. We know, we miss the old turf class too. Sniffle.


The Riparian Area is the land that is a specified distant from waterbodies (lakes, large rivers) and water courses (streams and rivers). Riparian Area, Riparian Zone, and Riparian Buffer are different terms that all refer to generally the same thing - land in proximity to water.
The riparian area is particularly important for water quality. A vegetated riparian zone results in cleaner water as vegetation filters and cleans water that runs off from the land before it reaches the stream, river, or lake. Other land cover types, such as developed and impervious surfaces, don't filter water while also contributing pollutants.
Riparian Area of a Basin/Watershed
First, the terms basin and watershed are often used interchangeably and both mean the area of land where runoff (rain, snow, etc.) drain to a common point. The riparian area
- is a subset of a basin
- is part of the basin and makes
- makes up a certain percentage of a basin.
Below is a visual example using the Hop Brook Watershed. The whole watershed is 11,139 acres (17.4 sq miles). The riparian area portion of the watershed is 2,951 acres (4.6 sq miles) or 26.5% of the watershed. The series of images demonstrate how the riparian area is created and used with the land cover.
- The watershed with its lakes and rivers that all drain to the comment point on the southeast of the watershed.
- The same watershed and waterways with the addition of the 300 foot riparian zone. It is includes all of the land that is 300 feet from any waterbody or stream.
- The same watershed shown over the Changing Landscape with NLCD land cover.
- The watershed and land cover with the addition of the riparian area.
- The watershed, riparian area, and ONLY land cover within the riparian area.
- Finally, just the riparian land cover. In summary, the riparian land cover is the land cover that is within 300 feet of any waterbody and stream. The riparian area is 26.5% of the full watershed.






The impervious surface layer is different from developed land cover classes.
Definition and Importance
Impervious surfaces, such as pavement, cement, and rooftops from roads, parking lots, and buildings, prevent infiltration of water into the soil, leading to stormwater runoff. When water from rain or snowmelt hits an impervious surface it runs off that surface picking up pollutants along the way and carrying them either directly or indirectly (via the stormwater system) to rivers, lakes, and Long Island Sound. In this way stormwater runoff poses both water quality (pollution) and water quantity (flooding) problems. These surfaces increase as we develop the landscape and are therefore closely related to – but not exactly the same as – developed land cover.
Impervious surface is an important map layer because it is the land cover most directly connected to the health of our waterways. There is a large body of scientific research that shows a strong relationship between the amount of impervious surface in a watershed and the health of the water resources in that watershed.
Impervious Surface Layer Method
The impervious surface layer is created by USGS as part of the Annual National Land Cover Database (NLCD). The NLCD impervious surface output represents fractional surface area of a pixel that is considered impervious and provides a value from 0-100 for every pixel mapped as one of the 4 developed categories (see next section). The value is equal to the percent of impervious in that pixel. The percent impervious per basin is calculated by finding the average percent impervious value within a basin and then multiplying the percent by the basin area. So, impervious surface is its own separate layer, derived from land cover but not one of the NLCD land cover classes. Learn more about Annual NLCD Fractional Impervious Surface from USGS.
Impervious Surface Layer vs Land Cover
Because of the size of the pixels in the land cover (30m by 30m, or about 100ft by 100ft), one developed pixel often contains a mixture of land covers such as some roof, some grass, some driveway, etc. This is called a mixed pixel. The land cover classification usually picks the most predominant option, but that also means that most developed pixels are not 100% impervious surface. The NLCD land cover has four developed classes. Notice that the definitions of the four classes include a range of impervious surface cover.
- High intensity: 80-100% impervious surface
- Medium intensity: 50-79% impervious surface
- Low intensity: 20-49%
- Developed open space: less than 20% impervious surface
| Developed, High Intensity | highly developed areas where people reside or work in high numbers. Examples include apartment complexes, row houses and commercial/industrial. Impervious surfaces account for 80% to 100% of the total cover. | |
| Developed, Medium Intensity | areas with a mixture of constructed materials and vegetation. Impervious surfaces account for 50% to 79% of the total cover. These areas most commonly include single-family housing units. | |
| Developed, Low Intensity | areas with a mixture of constructed materials and vegetation. Impervious surfaces account for 20% to 49% percent of total cover. These areas most commonly include single family housing units. | |
| Developed, Open Space | areas with a mixture of some constructed materials, but mostly vegetation in the form of lawn grasses. Impervious surfaces account for less than 20% of total cover. These areas most commonly include large-lot single-family housing units, parks, golf courses, and vegetation planted in developed settings for recreation, erosion control, or aesthetic purposes. |
The impervious surface layer turns those 4 classes into 100 classes therefore providing greater detail and specificity in the impervious surface mapping.

Below in an example showing Waterbury, CT. The graphics compare the impervious surface layer to the land cover.
- The fractal impervious surface map of the area. Pink pixels have lower percentages of impervious surface where dark reds and purples have higher percentages.
- The land cover of the same area. Notice the four developed land cover classes correlate with the impervious surface map of the same area (1), but with less detail.
- The same area on the original land cover map where there is one class of developed (red). Although the footprint is similar, it clearer contains less detail.
- A zoom in of the Waterbury, CT area showing impervious surface. The range of values along the continuum are evident from light to medium reds, darker reds, and many shades of purple. Each shade has a values of percent impervious.
- The zoom in on the land cover map of the same area. The four developed classes are evident. Note the extra detail in the previous image.





How do I Download Data or Connect to Services?
Download and map services are intended for GIS users.
Services
There are several places to find the services that are part of the Land Cover Map Viewer and Data Dashboards.
CT ECO Services page - Look for the Land Cover category and any services that include Changing Landscape with NLCD.
CT ECO ArcGIS Online Organization- Go to the Gallery and Look for services that pertain to Changing Landscape with NLCD. Many of these items are also available on the CT Geodata Portal.
NLCD services via MRLC - The NLCD services are also available directly from the MRLC website in WMS format. The page includes instructions as connecting to these services. Note that this is not a CT ECO service and any problems or questions should be directed to USGS.
Download
Download land cover data from USGS and the Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics Consortium (MRLC). Land cover data is designed to be viewed and analyzed withing GIS (Geographic Information System) software or similar. To view the land cover for the country, visit the MRLC Map Viewer.
More Information about NLCD Land Cover
Annual National Land Cover Database (NLCD) Collection 1 Products (ver.1.1, June 2025) Report | pdf
Annual NLCD Information from the Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics Consortium (MRLC)
Summary Tables
The Long Island Sound Watershed is the drainage area for Long Island Sound, which means that any water or rain in the watershed may eventually flow into Long Island Sound. Long Island Sound is the body of water between the Connecticut shoreline and the north shore of Long Island in New York. The Long Island Sound Watershed starts in Canada and includes potions of Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, New York, and Rhode Island. It is 16,455 square miles.
| Area in watershed* (sq miles) |
Percent of state in watershed* |
Percent of watershed* covered by the state |
|
| VT | 3933.1 | 41.1% | 23.9% |
| NH | 3060.1 | 33.0% | 18.6% |
| MA | 3470.0 | 42.9% | 21.1% |
| CT | 4943.7 | 99.5% | 30.0% |
| NY | 675.8 | 1.4% | 4.1% |
| RI | 371.8 | 34.5% | 2.3% |
*Watershed refers to the Long Island Sound Watershed

Long Island Sound Watershed (white hatch) over states.
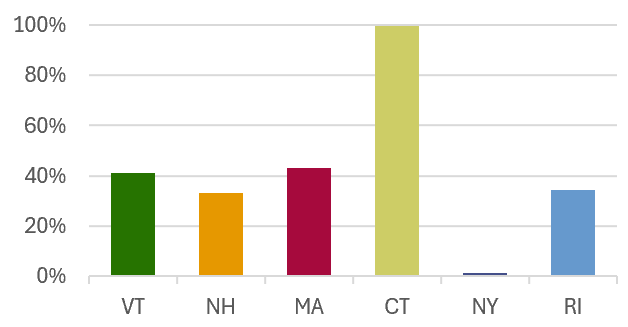
Percent of state in the Long Island Sound Watershed
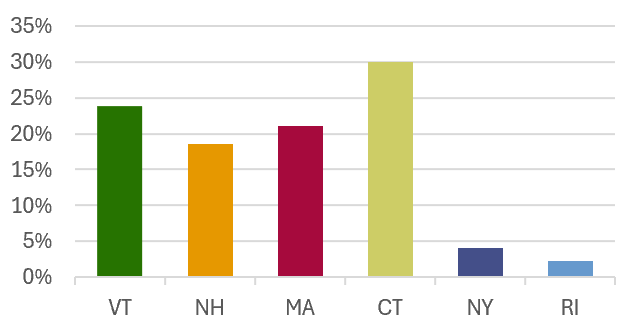
Percent of Long Island Sound Watershed
in State
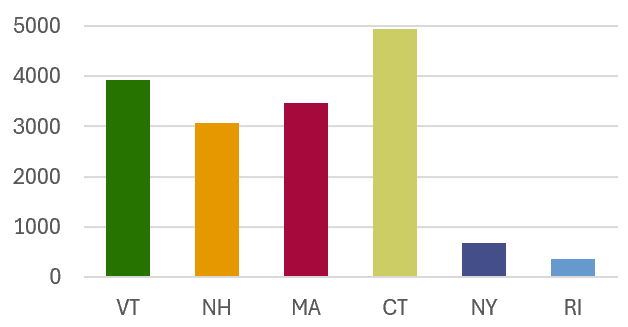
State Area (sq. miles) in the
Long Island Sound Watershed
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at land cover statistics.
Land Cover Stats: Long Island Sound Watershed Summary

Long Island Sound Watershed Land Cover Summary
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at the land cover statistics.
Area is in square miles. See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developed |
1041.7 | 1075.0 | 1096.6 | 1138.3 | 1196.0 | 1230.3 | 1248.8 | 1267.9 | 1280.0 | +238.3 | |
| 6.3% | 6.5% | 6.6% | 6.9% | 7.2% | 7.4% | 7.6% | 7.7% | 7.7% | +1.4% | ||
| Developed Open Space |
1368.3 | 1375.9 | 1401.2 | 1411.0 | 1416.1 | 1430.0 | 1446.1 | 1463.5 | 1472.3 | +103.9 | |
| 8.3% | 8.3% | 8.5% | 8.5% | 8.6% | 8.6% | 8.7% | 8.9% | 8.9% | +0.6% | ||
| Grasses |
88.9 | 87.1 | 95.3 | 88.3 | 87.2 | 113.2 | 105.0 | 113.5 | 102.7 | +13.8 | |
| 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.6% | +0.1% | ||
| Agriculture |
1128.5 | 1110.3 | 1097.0 | 1088.0 | 1078.8 | 1061.0 | 1047.2 | 1033.8 | 1025.7 | -102.8 | |
| 6.8% | 6.7% | 6.6% | 6.6% | 6.5% | 6.4% | 6.3% | 6.3% | 6.2% | -0.6% | ||
| Forest |
12363.9.0 | 12338.6 | 12298.5 | 12258.1 | 12202.9 | 12148.6 | 12136.3 | 12105.8 | 12102.1 | -261.8 | |
| 74.7% | 74.6% | 74.4% | 74.1% | 73.8% | 73.4% | 73.4% | 73.2% | 73.2% | -1.5% | ||
| Water |
416.1 | 422.8 | 419.3 | 73.5 | 424.0 | 417.2 | 413.9 | 411.7 | 411.4 | -4.8 | |
| 2.5% | 2.6% | 2.5% | 2.6% | 2.6% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 0% | ||
| Wetland |
76.4 | 75.3 | 75.5 | 73.5 | 74.2 | 77.6 | 79.7 | 80.1 | 81.4 | +4.9 | |
| 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0% | ||
| Barren |
58.3 | 57.3 | 58.9 | 60.2 | 62.9 | 64.4 | 65.1 | 65.9 | 66.7 | +8.5 | |
| 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | +0.8% |
Area is in square miles.
See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious |
588.6 | 607.7 | 621.5 | 642.5 | 670.1 | 687.8 | 697.4 | 707.4 | 713.3 | ||
| 3.6% | 3.7% | 3.8% | 3.9% | 4.1% | 4.2% | 4.2% | 4.3% | 4.3% | 1.4% |
Land Cover Stats: CT within the Long Island Sound Watershed

CT Portion of the Long Island Sound Watershed Land Cover Summary
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at the land cover statistics.
Connecticut is 99.5% within the Long Island Sound Watershed. 4944 square miles of Connecticut are part of the Long Island Sound Watershed which is 30% of the Long Island Sound Watershed.
Area is in square miles. See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developed |
532.0 | 552.0 | 563.9 | 587.0 | 619.3 | 638.2 | 647.7 | 658.5 | 655.0 | +133.0 | |
| 10.8% | 11.2% | 11.4% | 11.9% | 12.5% | 12.8% | 13.1% | 13.3% | 13.5% | +2.7% | ||
| Developed Open Space |
733.0 | 734.7 | 747.1 | 752.5 | 754.6 | 760.7 | 767.7 | 775.0 | 779.2 | +46.2 | |
| 14.8% | 14.9% | 15.1% | 15.2% | 15.3% | 15.4% | 15.5% | 15.7% | 15.8% | +0.9% | ||
| Grasses |
16.3 | 14.8 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 15.8 | 16.8 | 18.6 | 22.5 | 23.1 | +6.7 | |
| 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.5% | +0.1% | ||
| Agriculture |
368.3 | 355.8 | 347.4 | 340.4 | 334.0 | 324.6 | 318.8 | 313.2 | 309.5 | -58.8 | |
| 14.8% | 7.2% | 7.0% | 6.9% | 6.8% | 6.6% | 6.5% | 6.3% | 6.3% | -1.2% | ||
| Forest |
3124.8 | 3115.4 | 3100.6 | 3077.9 | 3048.6 | 3033.1 | 3021.4 | 3005.4 | 2998.1 | -126.7 | |
| 63.2% | 63.0% | 62.7% | 62.3% | 61.7% | 61.4% | 61.1% | 60.8% | 60.6% | -2.6% | ||
| Water |
118.1 | 120.1 | 119.0 | 120.2 | 119.4 | 116.8 | 115.6 | 115.4 | 114.3 | -3.8 | |
| 2.4% | 2.4% | 2.4% | 2.4% | 2.4% | 2.4% | 2.3% | 2.3% | 2.3% | -0.1% | ||
| Wetland |
35.0 | 34.5 | 24.7 | 34.0 | 34.3 | 35.4 | 35.7 | 35.6 | 36.1 | +1.1 | |
| 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.0% | ||
| Barren |
16.2 | 16.4 | 16.5 | 16.8 | 17.8 | 18.0 | 18.2 | 18.2 | 18.4 | +2.2 | |
| 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.0% |
Area is in square miles.
See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious |
300.1 | 311.7 | 319.3 | 331.1 | 346.8 | 356.7 | 361.5 | 367.0 | 370.1 | +69.9 | |
| 6.1% | 6.3% | 6.5% | 6.7% | 7.0% | 7.2% | 7.3% | 7.4% | 7.5% | +1.4% |
Land Cover Stats: NY within the Long Island Sound Watershed

New York Portion of the Long Island Sound Watershed Land Cover Statistics
New York is 1.4% within the Long Island Sound Watershed. 676 square miles of New York are part of the Long Island Sound Watershed which is 4.1% of the Long Island Sound Watershed.
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at the land cover statistics.
Area is in square miles. See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developed |
185.6 | 188.5 | 190.1 | 194.9 | 199.5 | 201.6 | 203.0 | 203.7 | 204.2 | +18.5 | |
| 27.5% | 27.9% | 28.1% | 28.8% | 29.5% | 29.8% | 30.0% | 30.1% | 30.2% | +2.7% | ||
| Developed Open Space |
162.1 | 161.7 | 162.8 | 161.9 | 159.9 | 159.7 | 160.2 | 161.4 | 161.7 | -0.4 | |
| 24.0% | 23.9% | 24.1% | 24.0% | 23.7% | 23.6% | 23.7% | 23.9% | 23.9% | -0.1% | ||
| Grasses |
2.7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.8 | -0.9 | |
| 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | -0.1% | ||
| Agriculture |
54.1 | 52.9 | 51.8 | 51.3 | 50.8 | 50.3 | 49.7 | 48.9 | 48.6 | -5.5 | |
| 8.0% | 7.8% | 7.7% | 7.6% | 7.5% | 7.4% | 7.4% | 7.2% | 7.2% | -0.8% | ||
| Forest |
245.3 | 244.5 | 243.2 | 240.4 | 238.4 | 237.4 | 236.5 | 235.8 | 235.0 | -10.3 | |
| 36.3% | 36.2% | 36.1% | 35.6% | 35.3% | 35.1% | 35.0% | 34.9% | 34.8% | -1.5% | ||
| Water |
10.6 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 10.7 | 10.7 | 10.7 | 11.0 | +0.4 | |
| 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | +0.1% | ||
| Wetland |
7.6 | 7.4 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.2 | -0.4 | |
| 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | -0.1% | ||
| Barren |
7.8 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 6.5 | 6.3 | -1.5 | |
| 1.2% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 0.9% | -0.2% |
Area is in square miles.
See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious |
111.5 | 113.2 | 114.2 | 116.5 | 118.8 | 120.0 | 120.9 | 121.7 | 122.0 | +10.5 | |
| 16.5% | 16.8% | 16.9% | 17.2% | 17.6% | 17.8% | 17.9% | 18.0% | 18.1% | +1.6% |
Land Cover Stats: RI within the Long Island Sound Watershed

Rhode Island Portion of the Long Island Sound Watershed Land Cover Statistics
Rhode Island is 34.5% within the Long Island Sound Watershed. 372 square miles of Rhode Island are part of the Long Island Sound Watershed which is 2.3% of the Long Island Sound Watershed.
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at the land cover statistics.
Area is in square miles. See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developed |
24.9 | 25.6 | 26.5 | 27.6 | 28.8 | 29.6 | 29.7 | 30.6 | 31.1 | +6.1 | |
| 6.7% | 6.9% | 7.1% | 7.4% | 7.8% | 8.0% | 8.0% | 8.2% | 8.4% | +1.7% | ||
| Developed Open Space |
31.3 | 32.2 | 33.0 | 33.6 | 35.0 | 35.7 | 36.8 | 37.7 | 38.3 | +7.0 | |
| 8.4% | 8.7% | 8.9% | 9.0% | 9.4% | 9.6% | 9.9% | 10.1% | 10.3% | +1.9% | ||
| Grasses |
6.4 | 6.1 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 6.3 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 6.2 | -0.2 | |
| 1.7% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.6% | 1.7% | 1.7% | -0.1% | ||
| Agriculture |
20.2 | 19.8 | 19.4 | 18.9 | 18.6 | 18.3 | 18.1 | 18.0 | 17.8 | -2.4 | |
| 5.4% | 5.3% | 5.2% | 5.1% | 5.0% | 4.9% | 4.9% | 4.8% | 4.8% | -0.7% | ||
| Forest |
272.9 | 272.0 | 270.7 | 268.7 | 266.4 | 265.1 | 264.2 | 262.2 | 261.5 | -11.4 | |
| 73.4% | 73.2% | 72.8% | 72.3% | 71.7% | 71.3% | 71.1% | 70.5% | 70.3% | -3.1% | ||
| Water |
9.6 | 9.5 | 9.4 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 9.3 | 9.3 | -0.3 | |
| 2.6% | 2.6% | 2.5% | 2.6% | 2.6% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | -0.1% | ||
| Wetland |
2.8 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.2 | +0.4 | |
| 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.9% | -0.1% | ||
| Barren |
3.9 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.4 | +0.8 | |
| 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.1% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% | +0.2% |
Area is in square miles.
See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious |
13.1 | 13.6 | 14.1 | 14.6 | 15.2 | 15.6 | 15.8 | 16.2 | 16.5 | +3.3 | |
| 3.5% | 3.7% | 3.8% | 3.9% | 4.1% | 4.2% | 4.3% | 4.4% | 4.4% | +0.9% |
Land Cover Stats: MA within the Long Island Sound Watershed

Massachusetts Portion of the Long Island Sound Watershed Land Cover Statistics
Massachusetts is 42.9% within the Long Island Sound Watershed. 3,470 square miles of Massachusetts are part of the Long Island Sound Watershed which is 21.1% of the Long Island Sound Watershed.
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at the land cover statistics.
Area is in square miles. See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developed |
179.1 | 185.2 | 189.2 | 196.7 | 207.7 | 214.3 | 218.3 | 221.1 | 225.0 | +45.9 | |
| 5.2% | 5.3% | 5.5% | 5.7% | 6.0% | 6.2% | 6.3% | 6.4% | 6.5% | +1.3% | ||
| Developed Open Space |
236.3 | 236.6 | 244.1 | 245.8 | 247.1 | 249.6 | 253.1 | 257.2 | 258.9 | +22.6 | |
| 6.8% | 6.9% | 7.0% | 7.1% | 7.1% | 7.2% | 7.3% | 7.4% | 7.5% | +22.6% | ||
| Grasses |
8.5 | 7.1 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 13.8 | 15.7 | 21.1 | 21.2 | +12.7 | |
| 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.6% | +0.4% | ||
| Agriculture |
245.5 | 242.5 | 237.9 | 236.6 | 234.9 | 231.6 | 228.9 | 226.1 | 224.2 | -21.3 | |
| 7.1% | 7.0% | 6.9% | 6.8% | 6.8% | 6.7% | 6.6% | 6.5% | 6.5% | -0.6% | ||
| Forest |
2672.0 | 2666.6 | 2662.9 | 2652.0 | 2638.9 | 2627.9 | 2621.7 | 2611.0 | 2608.4 | -63.6 | |
| 77.0% | 76.9% | 76.7% | 76.4% | 76.1% | 75.7% | 75.6% | 75.2% | 75.2% | -1.8% | ||
| Water |
97.5 | 101.6 | 100.1 | 103.0 | 102.9 | 100.4 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 97.2 | -0.4 | |
| 2.8% | 2.9% | 2.9% | 3.0% | 3.0% | 2.9% | 2.8% | 2.9% | 2.8% | 0.0% | ||
| Wetland |
15.3 | 14.9 | 14.8 | 14.1 | 14.6 | 16.2 | 17.3 | 17.2 | 18.2 | +2.9 | |
| 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | +0.1% | ||
| Barren |
15.8 | 13.5 | 14.4 | 14.9 | 15.6 | 16.1 | 16.3 | 16.5 | 17.0 | +1.2 | |
| 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.0% |
Area is in square miles.
See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious |
98.2 | 101.7 | 104.1 | 107.9 | 113.1 | 116.5 | 118.4 | 120.4 | 121.7 | +23.4 | |
| 2.8% | 2.9% | 3.0% | 3.1% | 3.3% | 3.4% | 3.4% | 3.5% | 3.5% | +1.7% |
Land Cover Stats: VT within the Long Island Sound Watershed

Vermont Portion of the Long Island Sound Watershed Land Cover Statistics
Vermont is 41.1% within the Long Island Sound Watershed. 3,933 square miles of Vermont are part of the Long Island Sound Watershed which is 23.9% of the Long Island Sound Watershed.
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at the land cover statistics.
Area is in square miles. See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developed |
64.0 | 65.4 | 66.9 | 69.3 | 73.3 | 75.6 | 77.6 | 79.0 | 79.9 | +15.9 | |
| 1.6% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.8% | 1.9% | 1.9% | 2.0% | 2.0% | 2.0% | +0.4% | ||
| Developed Open Space |
121.0 | 122.3 | 124.5 | 126.0 | 127.1 | 130.2 | 132.2 | 134.4 | 135.3 | +14.3 | |
| 3.1% | 3.1% | 3.2% | 3.2% | 3.2% | 3.3% | 3.4% | 3.4% | 3.4% | +0.4% | ||
| Grasses |
32.0 | 33.0 | 33.9 | 24.7 | 23.5 | 30.4 | 29.1 | 30.3 | 23.9 | -8.1 | |
| 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.9% | 0.6% | 0.6% | 0.8% | 0.7% | 0.8% | 0.6% | -0.2% | ||
| Agriculture |
300.8 | 300.1 | 301.1 | 301.5 | 301.3 | 298.6 | 295.5 | 292.8 | 291.7 | -0.2 | |
| 7.7% | 7.6% | 7.7% | 7.7% | 7.7% | 7.6% | 7.5% | 7.4% | 7.4% | -0.6% | ||
| Forest |
3373.7 | 3370.2 | 3364.8 | 3368.9 | 3364.9 | 3355.1 | 3355.0 | 3353.1 | 3358.0 | -15.7 | |
| 85.8% | 85.7% | 85.6% | 85.7% | 85.6% | 85.3% | 85.3% | 85.3% | 85.4% | -0.4% | ||
| Water |
29.4 | 29.6 | 29.3 | 30.0 | 29.9 | 29.6 | 29.3 | 28.6 | 29.3 | -0.1 | |
| 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.7% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.0% | ||
| Wetland |
6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 6.4 | 6.5 | 6.9 | 7.1 | 7.0 | +0.5 | |
| 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.0% | ||
| Barren |
5.7 | 5.9 | 6.2 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 7.8 | 8.0 | +2.3 | |
| 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | +0.1% |
Area is in square miles.
See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious |
35.1 | 36.0 | 36.9 | 38.1 | 39.8 | 41.0 | 42.0 | 42.6 | 43.1 | +7.9 | |
| 0.9% | 0.9% | 0.9% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 1.1% | +0.2% |
Land Cover Stats: NH within the Long Island Sound Watershed

New Hampshire Portion of the Long Island Sound Watershed Land Cover Statistics
New Hampshire is 33.0% within the Long Island Sound Watershed. 3,060 square miles of New Hampshire are part of the Long Island Sound Watershed which is 18.6% of the Long Island Sound Watershed.
See the Data Dashboards for a complete and interactive look at the land cover statistics.
Area is in square miles. See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developed |
54.5 | 56.7 | 58.5 | 61.4 | 65.9 | 69.3 | 70.9 | 72.3 | 73.3 | +18.8 | |
| 1.8% | 1.9% | 1.9% | 2.0% | 2.2% | 2.3% | 2.3% | 2.4% | 2.4% | +0.6% | ||
| Developed Open Space |
84.6 | 86.1 | 89.6 | 91.2 | 92.4 | 93.9 | 95.9 | 97.8 | 98.7 | +14.1 | |
| 2.8% | 2.8% | 2.9% | 3.0% | 3.0% | 3.1% | 3.1% | 3.2% | 3.2% | +0.5% | ||
| Grasses |
22.9 | 23.8 | 31.9 | 33.2 | 31.4 | 43.9 | 33.8 | 31.4 | 26.4 | +3.5 | |
| 0.8% | 0.8% | 1.0% | 1.1% | 1.0% | 1.4% | 1.1% | 1.0% | 0.9% | +0.1% | ||
| Agriculture |
139.5 | 139.2 | 139.4 | 139.4 | 139.2 | 137.6 | 136.1 | 134.8 | 133.9 | -5.6 | |
| 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.5% | 4.5% | 4.4% | 4.4% | -0.2% | ||
| Forest |
2675.0 | 2669.8 | 2656.2 | 2650.1 | 2645.5 | 2629.7 | 2637.4 | 2638.2 | 2641.0 | -34.0 | |
| 87.4% | 87.3% | 86.8% | 86.6% | 86.5% | 85.9% | 86.2% | 86.2% | 86.3% | -1.1% | ||
| Water |
68.4 | 68.6 | 67.9 | 68.1 | 68.5 | 67.5 | 67.4 | 66.2 | 67.3 | -1.1 | |
| 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 2.2% | 0.0% | ||
| Wetland |
7.0 | 7.0 | 7.2 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 7.7 | +0.7 | |
| 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.0% | ||
| Barren |
8.1 | 8.8 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.4 | 10.8 | 11.0 | 11.4 | 11.7 | +3.6 | |
| 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | 0.4% | +0.1% |
Area is in square miles.
See above for class descriptions.
Class |
1985 |
1990 |
1995 |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2023 |
Change
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious |
29.5 | 30.7 | 32.0 | 33.4 | 35.5 | 37.1 | 37.9 | 38.6 | 39.1 | +9.5 | |
| 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.0% | 1.1% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.3% | 1.3% | +0.3% |
